Glossary
- galley
- A long, narrow, single-decked ship propelled by oars as well as sails.
- Gallipoli
- The fortified harbor of Gallipoli guarded the narrow straits leading from the Aegean Sea to the Sea of Marmora and Constantinople. Controlled by the Ottoman Turks, it was a natural crossing place for armies going back and forth between Europe and Asia Minor.
- Genoa
- With one of the best harbors in the Mediterranean, the city of Genoa was a constant and fearsome commercial rival of Venice.
- gondola
- A boat or skiff with upturned bow and stern, normally propelled with one oar, traditionally used on the canals of Venice.
- grapple
- To hook or hold onto another ship or object with a grappling hook or iron, normally prior to boarding and fighting at close quarters.
- Greek Orthodox Church
- Also called the Eastern Orthodox Church, which split from the Roman Catholic Church in the Great Schism of 1054 as a result of disputes over religious doctrine and the authority of the pope in Rome.
- Gregorian calendar
- The solar calendar introduced by Pope Gregory XIII in 1582 to rectify errors in the Julian calendar.
- grosso
- A Venetian silver coin, referred by Michael in his mathematical problems as a denaro. The grosso fit into two accounting systems: In the ducat system it was accounted as 32 piccoli, and 24 grossi were equal to the ducat. In the lira di moneta system, it was equal to 2 soldi or 24 piccoli, and 10 grossi were equal to the lira. Pl. grossi.
- Guard Fleet
- The Guard (varda) was the military navy of Venice; it was usually referred to as the Gulf fleet, since the Adriatic Sea was called the Venetian Gulf.
- halyard
- A rope or tackle used to hoist a sail.
- hatch
- An opening in a ship's deck giving entrance to the compartment below.
- higher-order equation
- An algebraic equation in which the quantities include powers above the first (e.g.,
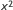 ,
, 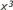 ,
, 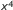 ).
).
- homo da remo
- Oarsman.
- homo de conseio
- Literally "man of the council," or "counselor," a senior non-noble officer on Venetian commercial galleys.
- hull
- The body of a ship, without masts, sails, or rigging.
- Hundred Years' War
- The period marked by a long series of wars fought between 1337 and 1453, principally between England and France.
- Julian calendar
- The calendar introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 B.C.E. in which the year has 365 days. Errors in this calendar caused it to get out of sync with actual astronomical events.
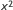 ,
, 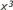 ,
, 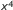 ).
).